Table of Contents
~~TOC~~
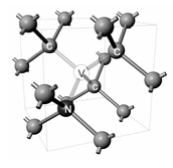
Diamond NV Centers
Basics
see also Nitrogen-vacancy center
Excitation
- wavelength 532nm
- excitation power should be 100 µW or above
Emission
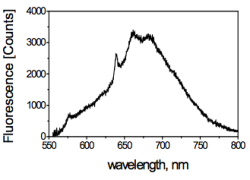
Figure 3 shows the emission spectra of a NV-center. The pronounced Peak at 637nm is the zero-phonon line of the diamond lattice (comparable to Raman).
- Emission filters therefor should be 650LP.
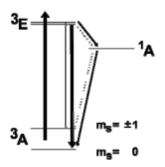
Fluorescence Lifetime
- Fluorescence Lifetime is approx. 12ns.
Measuring NV centers
Due to their photo-physical stability the NV-ceneters make for excellent demonstration samples for antibunching measurements. They are also potential candidates to image the confocal volume.
The following will explain how to find and measure NV-centers in bulk diamond.
System setup
- refractive index of diamond is 2.4. that means oil immersion is necessary as well as a high N.A.
- used objective: N.A. 1.3 is working, better 1.45 oil!
- Although measurements were possible also with the water immersion objective: with 60×1.2 water less than 50% count rate in comparison to 100×1.3 oil
- 0.95 N.A. air objective did not yield any usable results.
- excitation source: 532 nm
- MOFA (40MHz - for finding the centers, later 10MHz (12ns fluorescence lifetime))
- excitation power: >7000 a.u. @ 40MHz, > 2000 a.u. @ 10MHz (basically as high as possible)
- major dichroic: 532 / 635
- emission bandpass: 690/70 (for antibunching measurements 2 bandpasses directly in front of detectors)
- objective: 1.3 N.A. oil immersion
Mounting the sample
sample is mounted directly on top of the objective (with immerision oil, without any coverslips etc.).
Imaging/ finding nv centers
- focus on the interface between oil and diamond (nice reflection should be visible due to refractive index mismatch between oil and diamond)
- when imaging the surface most likely fluorescent spots will be found. Those are probably dirt and unlike the NV-centers will bleach in a matter of seconds. They also have a shorter fluorescence lifetime.
- move approx. 5 micrometer into the sample.
- Although photo-physical stability makes the nv-centers ideal single emitter samples compared to single molecules the laser power to excite them has to be considerably higher. (0.1 mW and above).
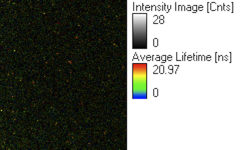
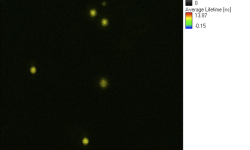
- Figure 4 shows a prescan of the complete field of view. The orange dots are NV-centers.
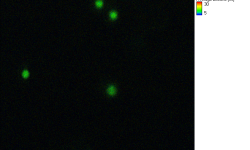
- zoom into a region with a few NV-centers (see figure 5),
- select one, and position the focus on the NV-center.
- use the oscilloscope and pifoc+piezo to move the NV-center in x,y and z into the center of the focus.
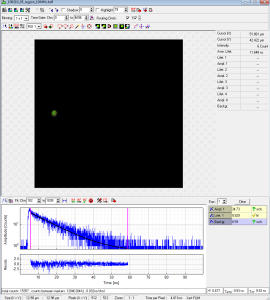
- For lifetime analysis switch laser repetition rate to 10MHz (see figure 6)
- check whether the fluorescence lifetime is around 12 ns.
- the NV-center's emission should stay stable (no bleaching)
Typical Measurement Results
- Prescan should look like figure 4
- smaller area is depicted in figure 5 and figure 6
- Selecting a ROI in figure 6 and plotting the fluorescence lifetime histogram should resemble figure 7
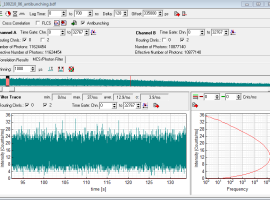
- when measuring the fluorescence intensity of a single NV center, the count rate should stay stable. The time trace in figure 8 shows a reduction of the countrate due to stage drift (temperature etc, or in this case probably because the MT200 inhouse II was mounted on a wheelbarrow instead of an optical table)
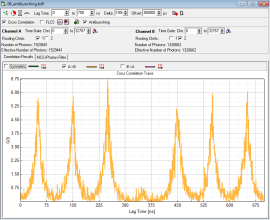
- to perform antibunching measurements on a selected NV-center choose a NV-center that is isolated, measuring time of 120 s should be enough to yield an antibunching measurement comparable to figure 9.
NOTE: Measurement setup has to be changed (see antibunching measurements)
References
M. Boersch, R. Reutera, G. Balasubramaniana, R. Erdmann, F. Jelezkoa, J. Wrachtrup Fluorescent nanodiamonds for FRET-based monitoring of a single biological nanomotor FoF1-ATP synthase Proc. of SPIE Vol. 7183, 71832N (2009)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/12.812720